Combustion Forklifts: Power and Performance in One Package
Internal combustion forklifts have long been a staple in the material handling industry, known for their robust power and performance. These forklifts, powered by gasoline, diesel, or liquid propane gas (LPG), offer several advantages that make them indispensable in various industrial settings. This article delves into the key benefits and features of combustion forklifts, highlighting why they remain a preferred choice for many businesses.
Unmatched Power and Efficiency
One of the primary reasons for the popularity of combustion forklifts is their superior power output. Unlike electric forklifts, which rely on battery power, combustion forklifts are driven by internal combustion engines that provide higher torque and horsepower. This enables them to handle heavier loads with greater efficiency, making them ideal for demanding applications such as construction, manufacturing, and warehousing.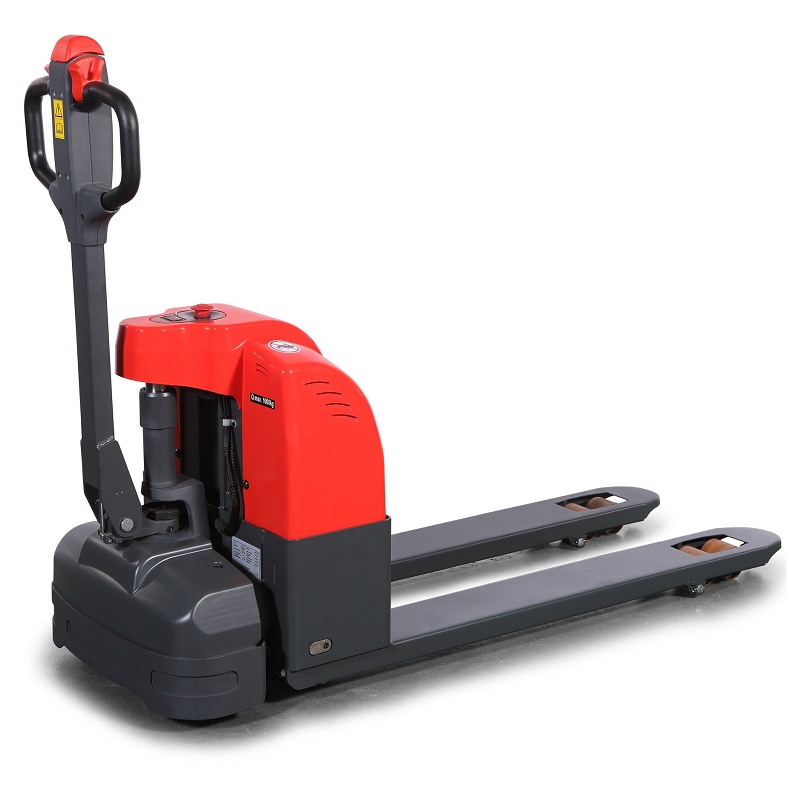 ForkLift | China Manufacturer Trade price on Materials Handling Fork-lifts Truck, Stackers, Industrial vehicles, Scrubbers, Transporters Sale Buy Online Industrial Equipment in USA/UK/India/Australia/canada | ForkLift
ForkLift | China Manufacturer Trade price on Materials Handling Fork-lifts Truck, Stackers, Industrial vehicles, Scrubbers, Transporters Sale Buy Online Industrial Equipment in USA/UK/India/Australia/canada | ForkLift
Combustion forklifts excel in environments where rapid acceleration and load-lifting capabilities are crucial. Their ability to operate continuously without the need for recharging is a significant advantage, especially in high-volume operations. This extended operating time ensures minimal downtime, enhancing overall productivity.
Versatility in Various Environments
Another notable advantage of combustion forklifts is their versatility. These forklifts can operate in a wide range of environments, including outdoor and harsh conditions where electric forklifts might struggle. For instance, in cold storage facilities or outdoor construction sites, combustion forklifts perform reliably, unaffected by extreme temperatures.
Moreover, combustion forklifts are not limited by the availability of charging infrastructure. As long as they have access to fuel, they can continue to operate, making them suitable for remote or off-grid locations. This flexibility is particularly beneficial for industries that require mobility and adaptability in their operations.
Cost-Effectiveness and Lower Maintenance
In terms of cost-effectiveness, combustion forklifts often have a lower initial purchase price compared to their electric counterparts. Additionally, the ongoing maintenance costs are generally lower. Electric forklifts require expensive battery replacements and regular charging infrastructure, whereas combustion forklifts do not. The cost of fuel is typically lower than electricity, further reducing operational expenses.
Combustion forklifts also benefit from longer lifespans due to their robust construction and fewer electronic components that can fail. This durability translates to lower long-term maintenance costs and a better return on investment for businesses.
Advanced Features and Safety
Modern combustion forklifts are equipped with advanced features that enhance their performance and safety. Emission control systems, such as catalytic converters, help reduce the emission of harmful pollutants, making them more environmentally friendly. These systems are essential for maintaining air quality, especially in enclosed spaces.
Safety is a paramount concern in material handling operations. Combustion forklifts come with various safety features, including overhead guards, seat belts, and load-sensing systems that prevent tip-overs and ensure stability during operation. These features contribute to a safer working environment, reducing the risk of accidents and injuries.
Applications Across Industries
Combustion forklifts are widely used across various industries due to their power, versatility, and reliability. In manufacturing plants, they handle heavy-duty applications such as lifting and transporting large materials. Warehouses benefit from their ability to move goods rapidly and efficiently, while the paper and pulp industry relies on them for handling heavy rolls of paper and other materials.