The Limitations of Traditional Training Methods:
Traditional training methods, such as classroom lectures and tabletop exercises, can provide some theoretical knowledge, but they often lack the realism and hands-on experience necessary for effective well control training. These methods may not adequately prepare personnel to react effectively in high-pressure, dynamic situations.
The Benefits of Realistic Simulation:
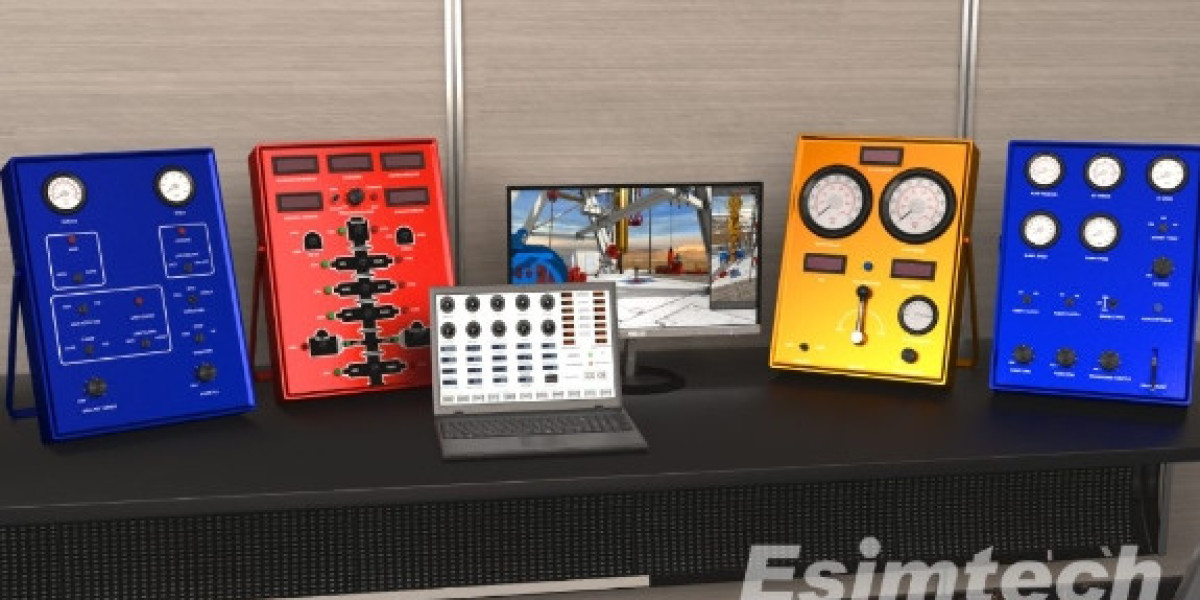
Enhanced Situational Awareness: Realistic simulations, such as those using drilling simulators or virtual reality (VR) technologies, provide a dynamic and immersive learning experience. Trainees can experience the sights, sounds, and pressures of a real-world well control incident, enhancing their situational awareness and decision-making skills.
Improved Decision-Making: Simulations allow trainees to make critical decisions in a safe and controlled environment. By experiencing the consequences of their actions, they can learn from their mistakes and refine their decision-making processes.
Enhanced Teamwork: Well control incidents often require coordinated teamwork. Simulations provide an opportunity for teams to practice their communication, coordination, and problem-solving skills in a realistic setting.
Cost-Effectiveness: While the initial investment in simulation technology may be significant, it can ultimately lead to cost savings by reducing the risk of real-world incidents, minimizing downtime, and improving operational efficiency.
Key Elements of Realistic Well Control Simulations:
High Fidelity: Simulations should accurately replicate the physical and operational characteristics of drilling rigs and well control equipment.
Dynamic Environments: Simulations should incorporate dynamic elements, such as changing well pressures, equipment failures, and unexpected events, to challenge trainees and prepare them for real-world scenarios.
Instructor-Led Feedback: Experienced instructors should provide real-time feedback to trainees, guiding them through the simulation and providing valuable insights.
Scenario-Based Training: Simulations should be based on real-world scenarios, allowing trainees to experience a wide range of challenges and develop the skills to handle them effectively.
Conclusion:
Realistic simulation technology is transforming well control training in the oil and gas industry. By providing a dynamic and immersive learning experience, simulations enhance situational awareness, improve decision-making, and foster teamwork. As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more sophisticated and impactful simulation solutions to be developed for well control training, further enhancing safety and operational efficiency.