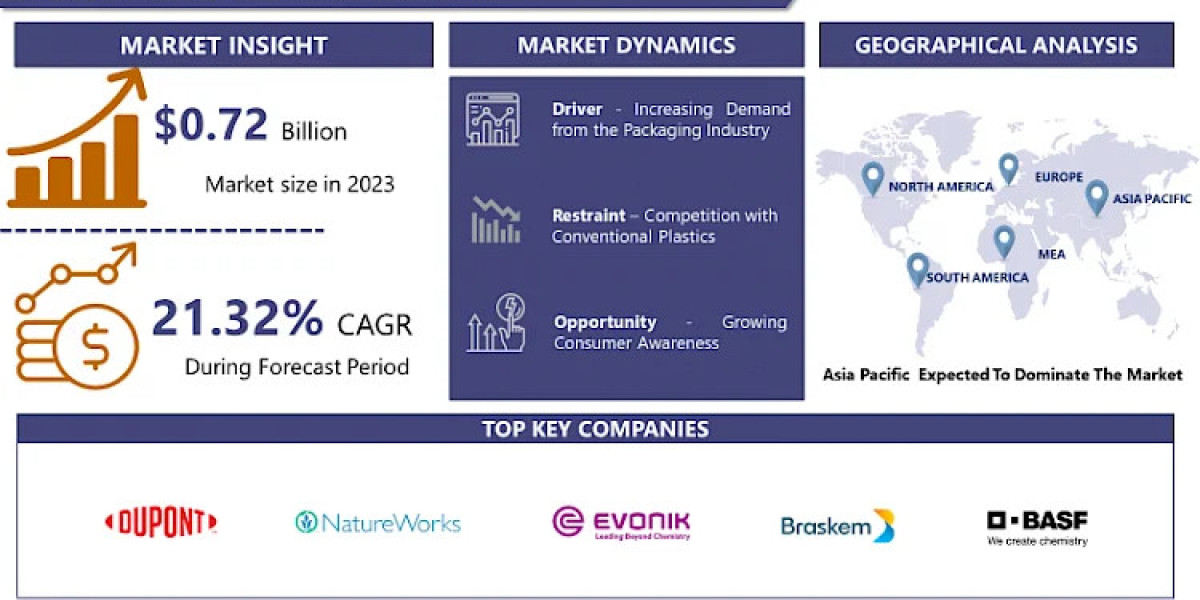
In agriculture, the health of a plant’s root system plays a pivotal role in determining its overall growth, productivity, and resilience. Farmers and gardeners have long relied on chemical fertilizers for quick nutrient boosts. Still, the rise of bio-fertilisers has brought a more sustainable and root-focused approach to farming. Bio-fertilizers from natural organisms work harmoniously with the soil and plants to promote healthier root development. This has sparked a shift from chemical-heavy practices to more organic and eco-friendly solutions.
What Are Bio-Fertilizers?
Bio-fertilizers are living organisms, such as bacteria, fungi, and algae, that naturally enrich the soil by fixing nutrients and stimulating plant growth. Unlike chemical fertilizers, which supply nutrients directly, bio-fertilizers enhance nutrient availability through biological processes.
Some common examples of bio-fertilizers include:
Nitrogen-fixing bacteria (e.g., Rhizobium): Converts atmospheric nitrogen into a usable form for plants.
Phosphate-solubilizing bacteria (e.g., Pseudomonas): Releases phosphorus bound in the soil, making it accessible to plants.
Mycorrhizal fungi: Forms symbiotic relationships with plant roots, increasing water and nutrient absorption.
Why Are Roots the Foundation of Plant Health?
Roots anchor plants, absorbing water and nutrients from the soil and supporting above-ground growth. Healthy roots ensure more vigorous plants and make crops more resistant to drought, pests, and diseases. Therefore, focusing on root development is essential for any successful farming or gardening practice.
Absorption of Nutrients and Water: Roots are the main pathway for plants to access essential elements like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium.
Support and Stability: A strong root system helps plants withstand harsh environmental conditions like strong winds or heavy rainfall.
Symbiotic Relationships: Roots provide a base for beneficial microbes, fostering a dynamic ecosystem within the soil.
How Bio-Fertilizers Improve Root Development
Bio-fertilizers excel at promoting healthy root growth because they work synergistically with the plant and soil. Unlike chemical fertilizers, which deliver nutrients instantly but can harm the soil in the long run, bio-fertilizers provide sustainable support for robust root systems.
1. Enhancing Nutrient Availability
Bio-fertilizers naturally release nutrients in a form that plants easily absorb. For example, nitrogen-fixing bacteria convert atmospheric nitrogen into ammonium, while phosphate-solubilizing bacteria break down insoluble phosphate in the soil.
This gradual nutrient release ensures that roots are not overloaded, promoting steady and healthy growth. Products like Super nova seaweed extract further enhance this process by stimulating microbial activity and improving soil structure, resulting in healthier roots and increased nutrient absorption.
2. Encouraging Root Symbiosis
Mycorrhizal fungi play a vital role in bio-fertilizer-based agriculture by forming a symbiotic relationship with plant roots. These fungi extend the root network through hyphae, effectively increasing the plant’s ability to absorb water and nutrients from a larger area. This partnership enhances root development and improves the plant’s resilience to stress.
3. Improving Soil Health
Bio-fertilizers enrich the soil with organic matter and beneficial microbes, creating a fertile environment for roots to thrive. Healthy soil is less prone to compaction and retains moisture better, allowing roots to penetrate more easily and access the necessary resources.
Bio-fertilizers reduce soil salinity and pH imbalances caused by excessive chemical fertilizer use.
They prevent nutrient leaching, ensuring essential elements stay in the root zone.
4. Stimulating Root Hormones
Certain biofertilizers produce growth hormones, such as auxins and cytokinins, directly stimulating root elongation and branching. This leads to a more extensive root system, allowing plants to access deeper soil layers and extract more nutrients and water.
Limitations of Chemical Fertilizers for Root Development
Chemical fertilizers, while effective in delivering immediate nutrients, can have long-term adverse effects on soil health and root systems.
1. Overload of Nutrients
Chemical fertilizers often deliver nutrients in excessive quantities, damaging delicate root tissues. Over time, this can reduce root efficiency and even plant stress.
2. Soil Degradation
Repeated chemical fertilizers can lead to soil compaction, reduced organic matter, and a loss of beneficial microbes. These factors create an inhospitable environment for roots, limiting their growth and function.
3. pH Imbalances
Many chemical fertilizers alter the pH of the soil, making it either too acidic or too alkaline. This imbalance can inhibit root growth and prevent the absorption of essential nutrients.
"Healthy soil is a living ecosystem, and bio-fertilizers are the key to nurturing it. We create a foundation for sustainable and productive farming by focusing on root development."
Benefits of Choosing Bio-Fertilizers Over Chemicals
Long-Term Sustainability
Bio-fertilizers improve soil health and fertility over time, creating a self-sustaining cycle that benefits plants and the environment.
Eco-Friendly Solution
Unlike chemical fertilizers, which can contribute to water pollution and greenhouse gas emissions, bio-fertilizers are natural and biodegradable, leaving no harmful residues.
Cost-Effectiveness
While chemical fertilizers may offer short-term results, their overuse often leads to diminished returns due to soil degradation. On the other hand, bio-fertilisers improve soil fertility and root health, reducing the need for repeated applications.
How to Use Bio-Fertilizers Effectively
For optimal results, it’s essential to use bio-fertilizers correctly. Here are some tips for integrating them into your farming practices:
Apply During Planting: Inoculate seeds or seedlings with bio-fertilizers to promote early root development.
Combine With Organic Matter: Adding compost or manure alongside bio-fertilizers enhances their effectiveness.
Monitor Soil Conditions: Conduct soil tests to identify nutrient deficiencies and choose the appropriate type of bio-fertilizer.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can bio-fertilizers replace chemical fertilizers entirely?
Bio-fertilizers can significantly reduce the need for chemical fertilizers but may not entirely replace them, especially in nutrient-deficient soils. Combining both in a balanced way often yields the best results.
2. Are bio-fertilizers safe for all crops?
Yes, bio-fertilizers are safe for all types of crops and can be used in both conventional and organic farming systems.
3. How long does it take for bio-fertilizers to show results?
Bio-fertilizers work gradually, improving soil health and root development over time. Visible improvements in plant health typically appear within a few weeks.
A New Era of Farming
The shift from chemical fertilizers to bio-fertilizers marks a new era in agriculture, where sustainability and productivity go hand in hand. Bio-fertilizers create a foundation for healthy plants, fertile soil, and abundant harvests by focusing on root development. Whether you’re a small-scale gardener or a large-scale farmer, embracing bio-fertilizers can transform your approach to plant nutrition and soil management.