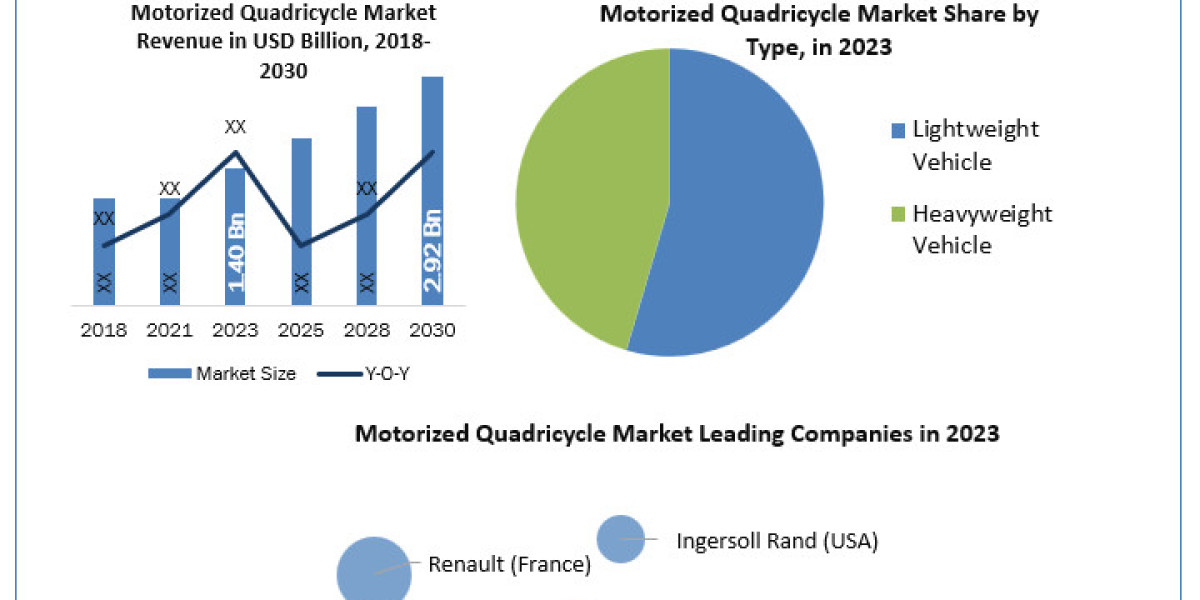
Understanding Trade Price on Materials: A Comprehensive Overview
Trade price, often referred to as the wholesale price, is a critical concept in the realm of commerce, particularly when it comes to materials. This price represents the amount paid by businesses to acquire raw materials or products from manufacturers or producers. Understanding trade price on materials is essential for businesses to manage costs, set competitive prices, and maintain profitability.
The Significance of Trade Price on Materials
Trade price on materials is the foundation of the pricing structure for many businesses. It directly impacts the cost of goods sold (COGS) and, consequently, the overall profitability of a company. By securing favorable trade prices, businesses can reduce their production costs and offer competitive prices to their customers. ForkLift Trucks.com | China Manufacturer Trade price on Materials Handling Fork-lifts Truck, Stackers, Industrial vehicles, Scrubbers, Transporters Sale Buy Online Industrial Equipment in USA/UK/India/Australia/canada
ForkLift Trucks.com | China Manufacturer Trade price on Materials Handling Fork-lifts Truck, Stackers, Industrial vehicles, Scrubbers, Transporters Sale Buy Online Industrial Equipment in USA/UK/India/Australia/canada
For manufacturers, trade price is a reflection of the costs incurred during the production process, including raw materials, labor, and overhead expenses. For retailers, it is the price at which they purchase goods to sell to end consumers. The difference between the trade price and the retail price is the markup, which covers the retailer’s operating expenses and profit margin.
Factors Influencing Trade Price on Materials
Several factors can influence the trade price of materials:
Production Costs: The cost of raw materials, labor, and manufacturing processes directly impacts the trade price. For instance, fluctuations in the price of metals like steel or aluminum can significantly affect the trade price of products that rely on these materials.
Market Demand and Supply: The balance between demand and supply in the market can affect trade prices. High demand and low supply often result in higher trade prices, while low demand and high supply can lead to lower trade prices.
Economic Conditions: Economic factors such as inflation, exchange rates, and economic growth can impact trade prices. For example, inflation can increase production costs, leading to higher trade prices.
Market Competition: The level of competition in the market can also influence trade prices. In highly competitive markets, manufacturers may offer lower trade prices to attract buyers and gain market share.
Trade Price vs. List Price
It is important to distinguish between trade price and list price. While trade price is the amount paid by businesses to acquire materials, list price is the suggested retail price that consumers should pay. The difference between these two prices is the profit margin, which covers the business’s costs and growth.
Businesses must carefully consider their markup to ensure they remain competitive while still covering their costs and making a profit. A higher markup can lead to higher retail prices, which may deter price-sensitive consumers. Conversely, a lower markup can attract more customers but may result in lower profit margins.
Strategies for Negotiating Trade Prices
Negotiating favorable trade prices is a critical skill for businesses. Effective negotiation can lead to cost savings and improved profitability. Here are some tips for negotiating trade prices:
Build Strong Relationships: Establishing good relationships with suppliers can lead to better trade prices. Suppliers may offer discounts or favorable terms to businesses they trust and value.
Volume Discounts: Purchasing in bulk can often result in lower trade prices. Suppliers may offer volume discounts to encourage larger orders.
Market Research: Conducting thorough market research can help businesses understand the prevailing trade prices and negotiate better deals.
Long-Term Contracts: Entering into long-term contracts with suppliers can provide stability and potentially lower trade prices. Suppliers may offer better terms for long-term commitments.
Conclusion
Trade price on materials is a crucial element in the pricing strategy of businesses. It affects the cost structure, profit margins, and competitiveness of companies. By understanding the factors influencing trade prices and employing effective negotiation strategies, businesses can optimize their pricing and improve their overall profitability.